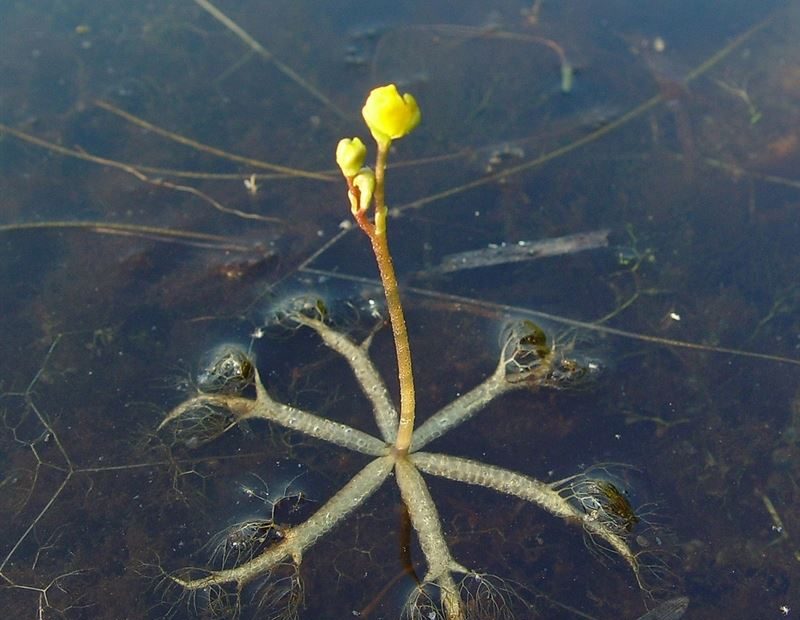
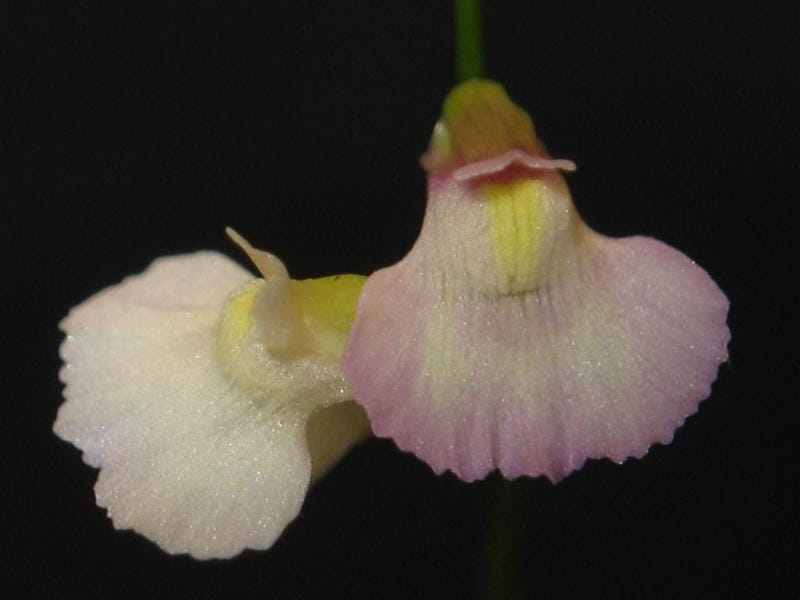
Bladderwort is a carnivorous aquatic plant that belongs to the family Lentibulariaceae. It grows in temperate and tropical regions, in standing or slowly flowing fresh water. It has divided leaves and yellow flowers. The stems and leaves contain small, bladder-like traps that use suction to capture small aquatic prey such as insect larvae, brine shrimp, and water fleas.
Bladderwort photos:
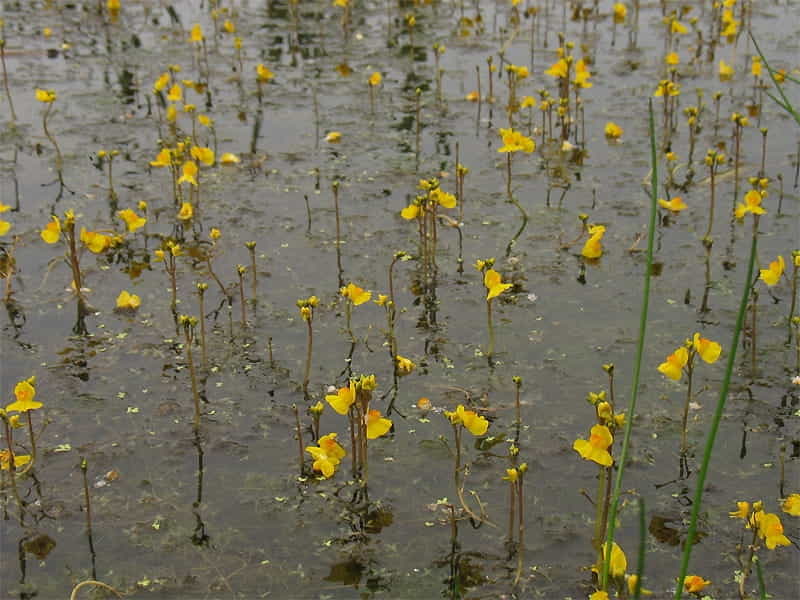
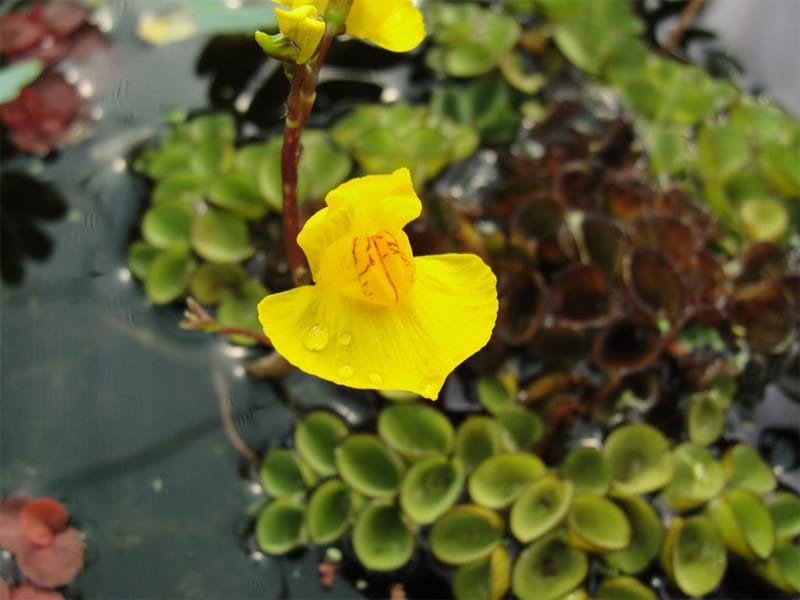
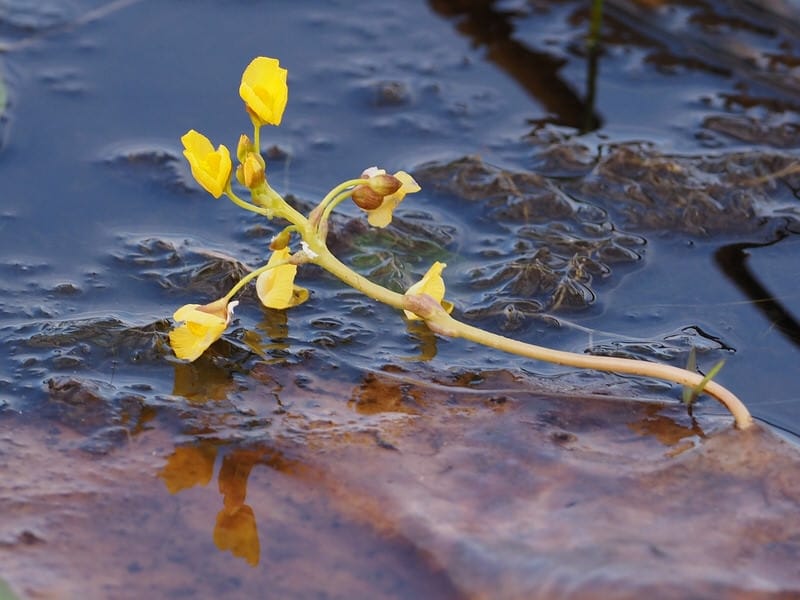
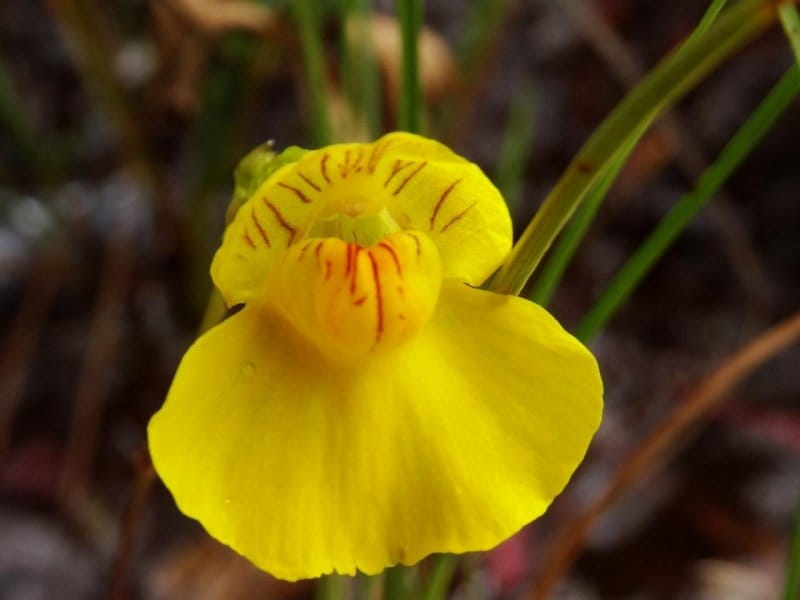
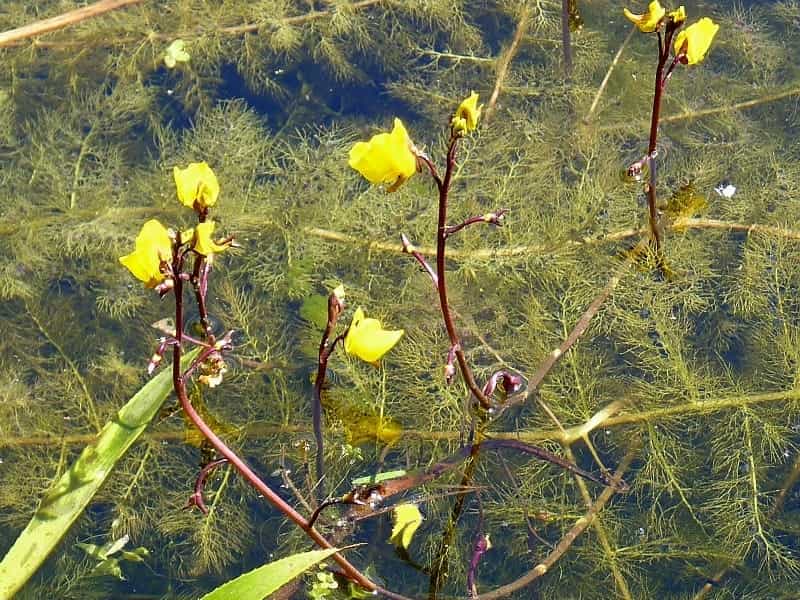
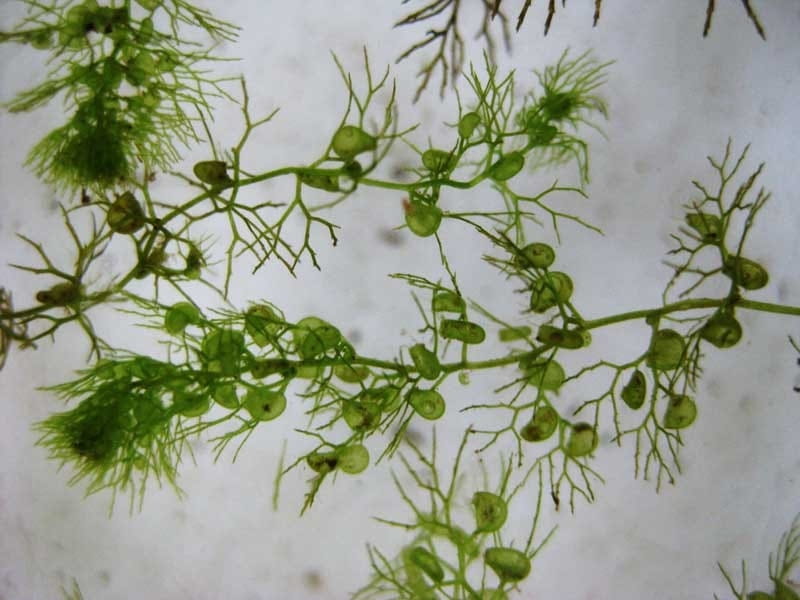
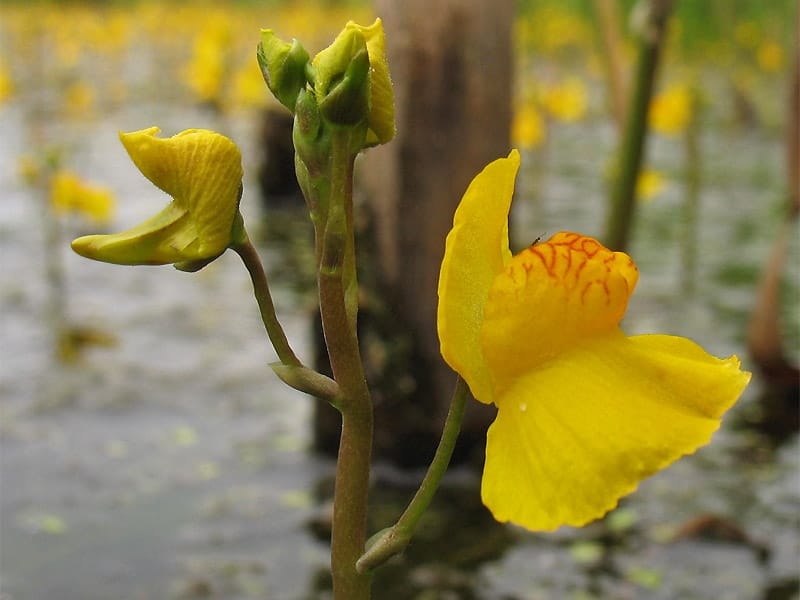
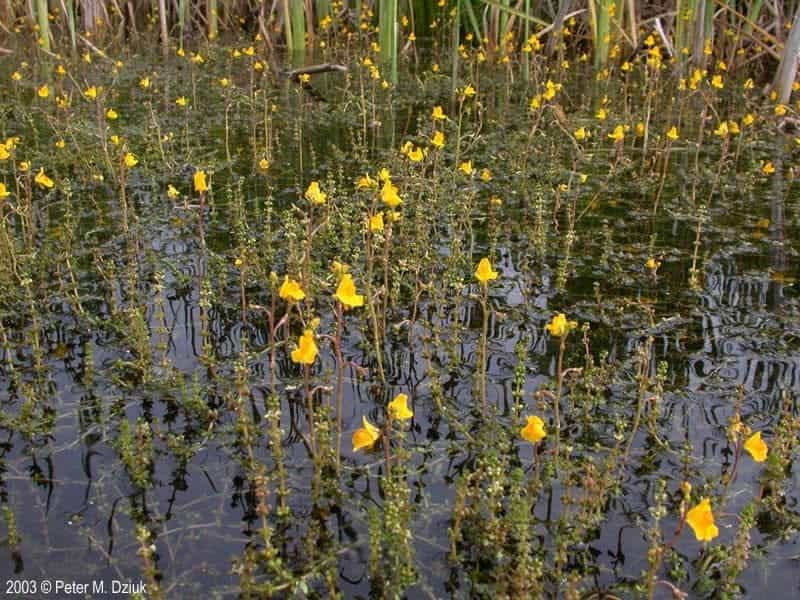
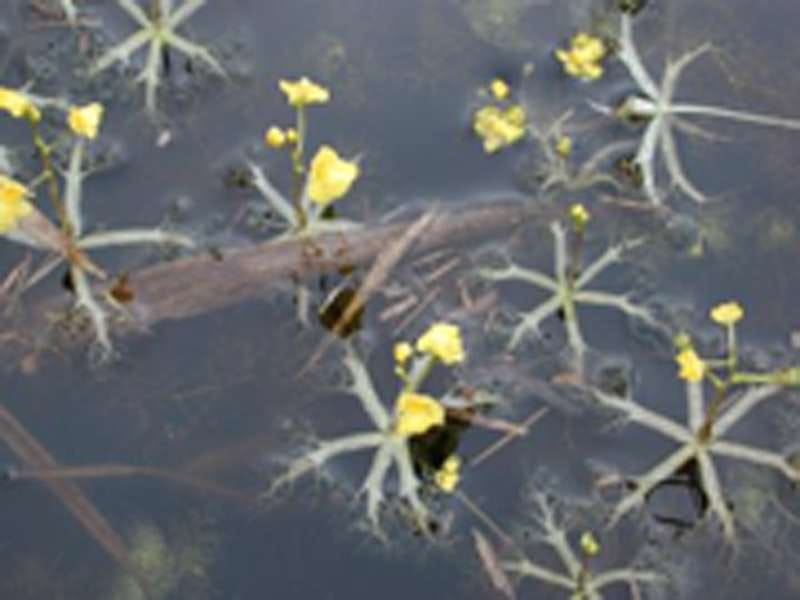
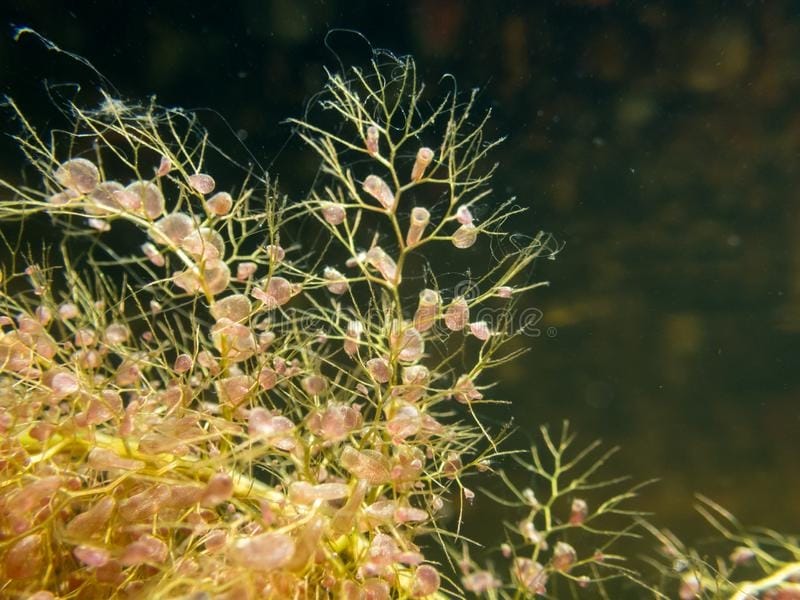
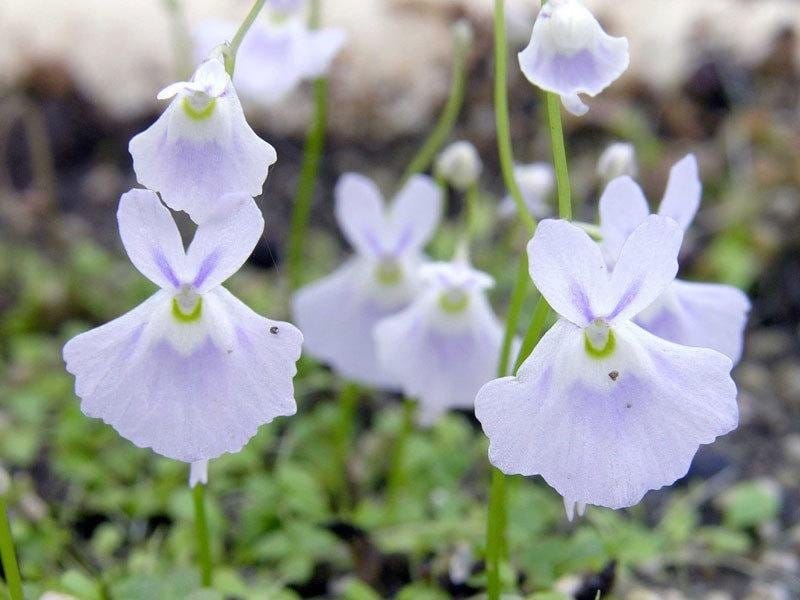
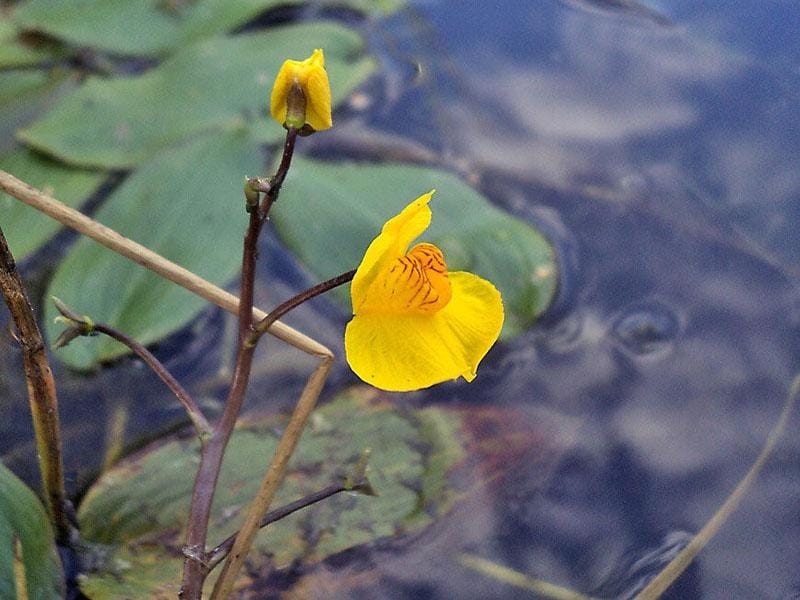
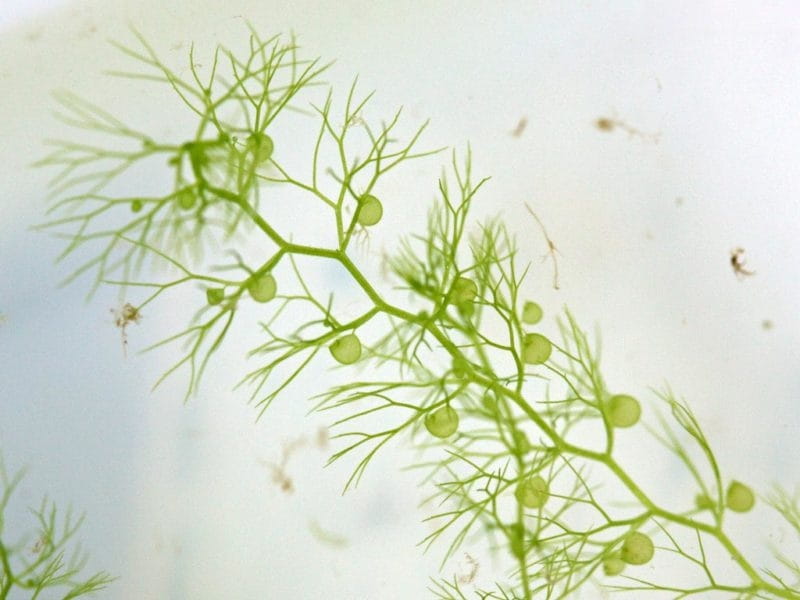
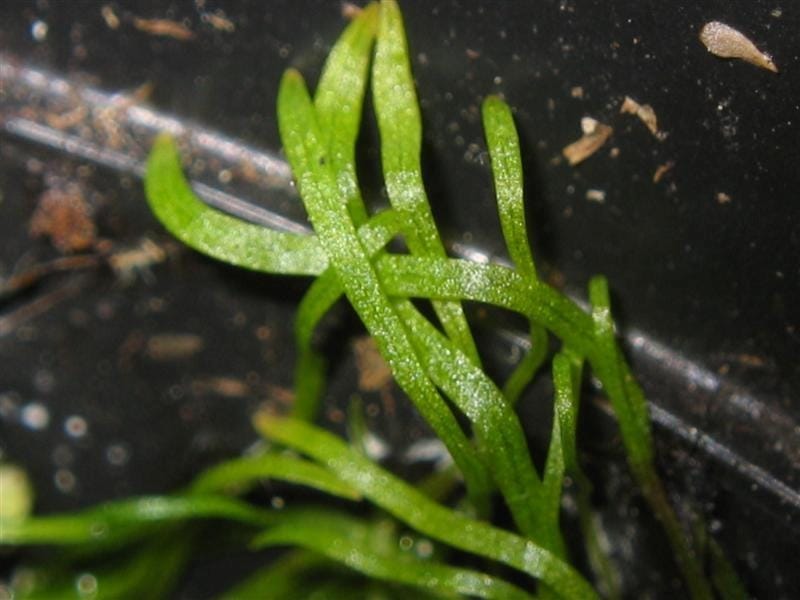
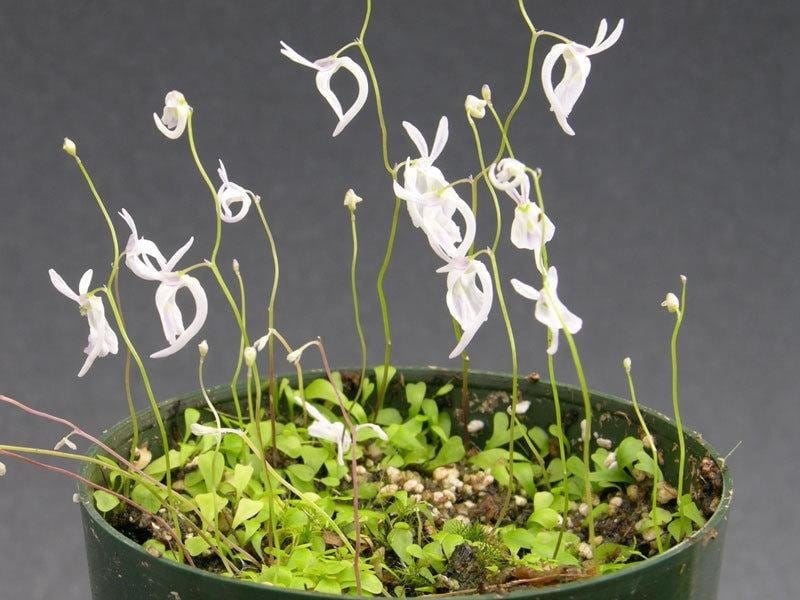
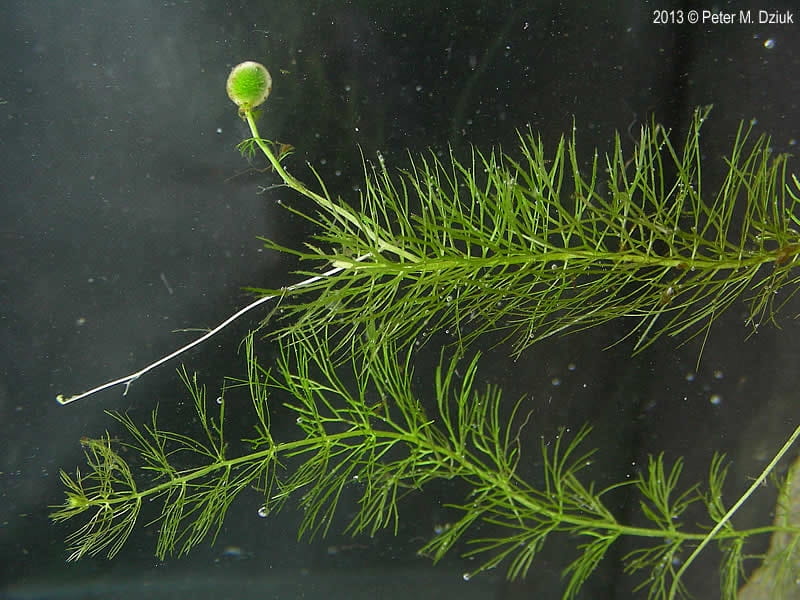
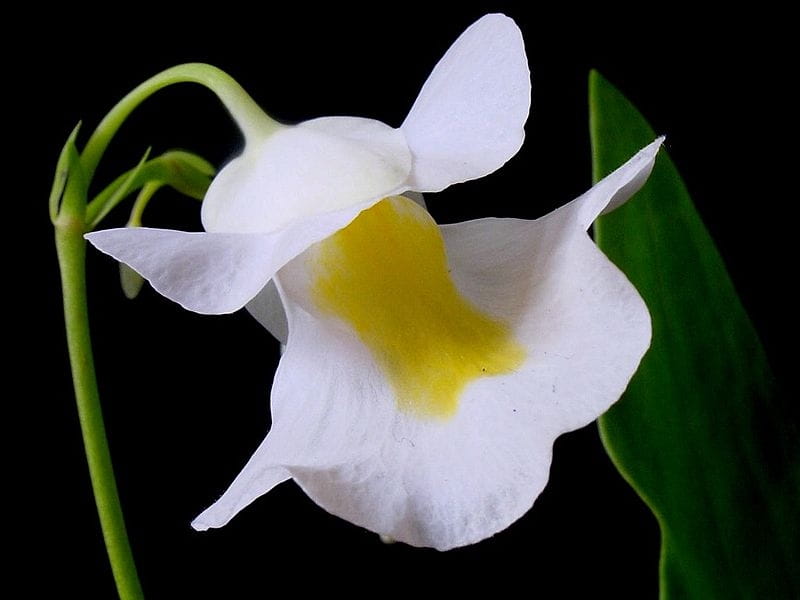
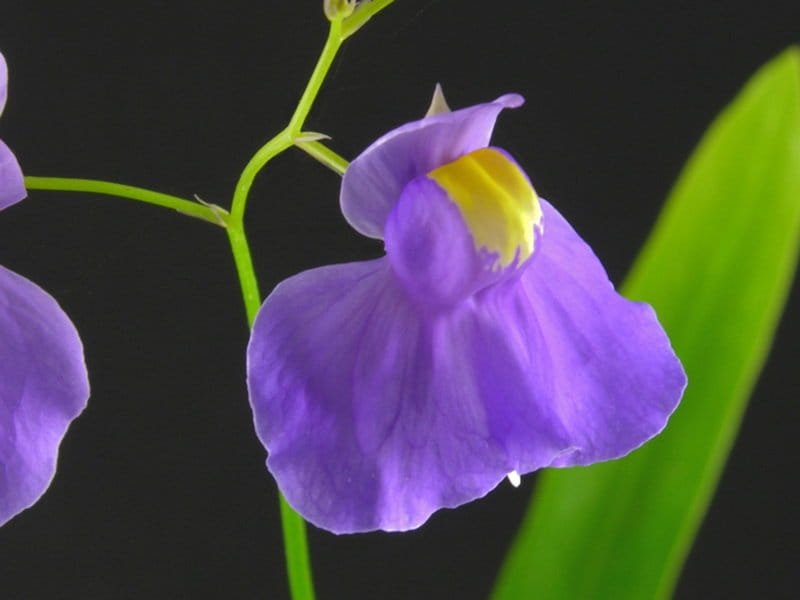
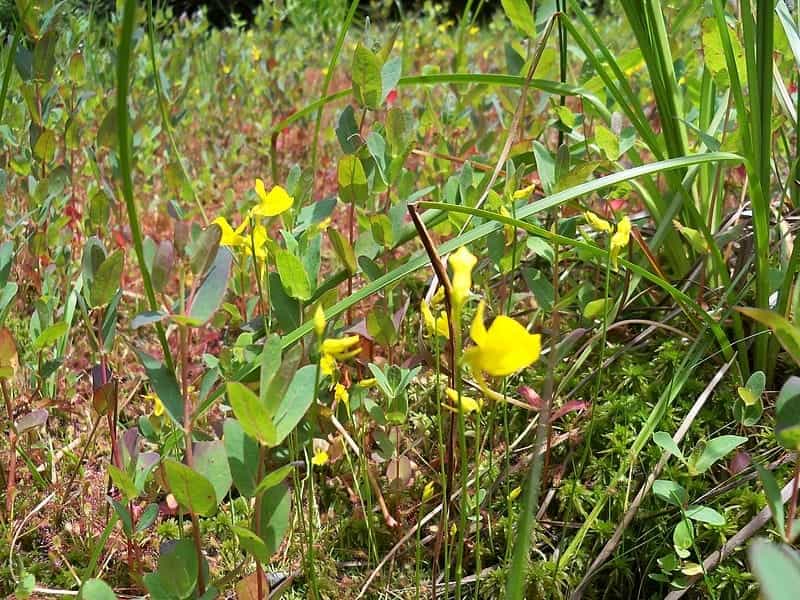
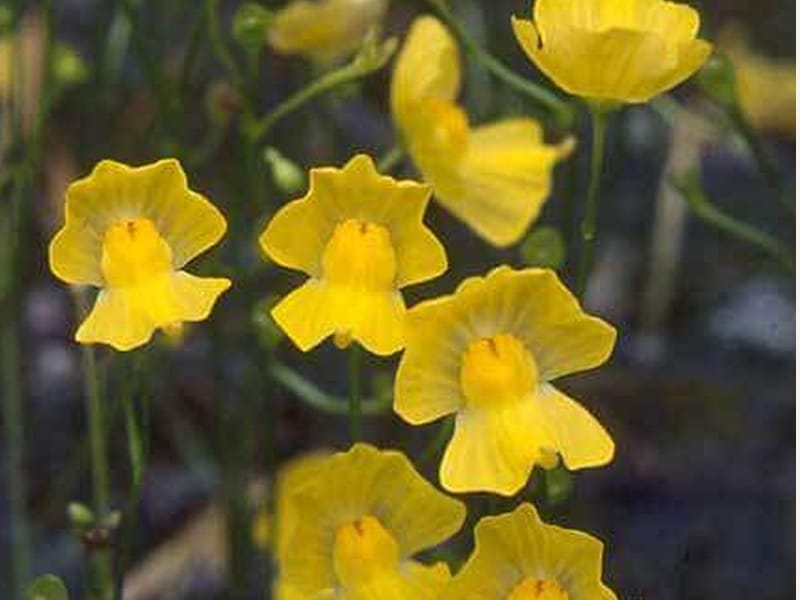


























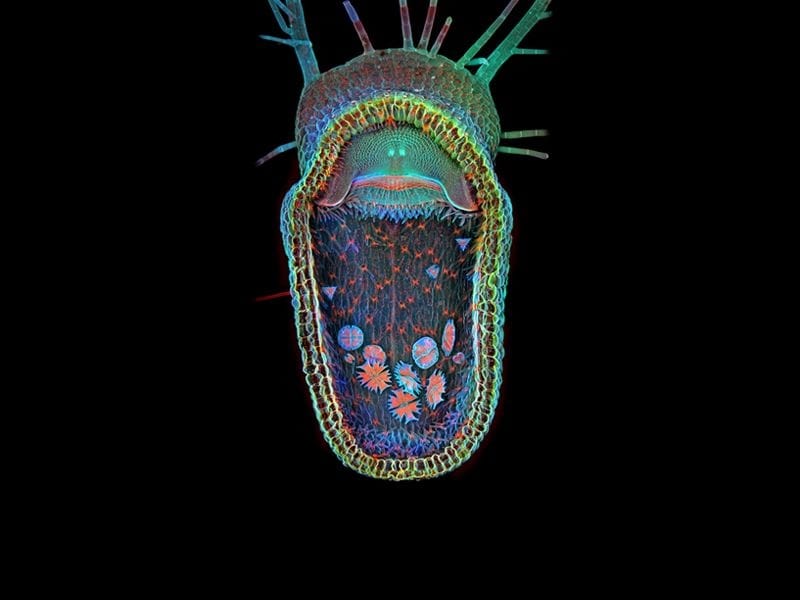


Adaptation
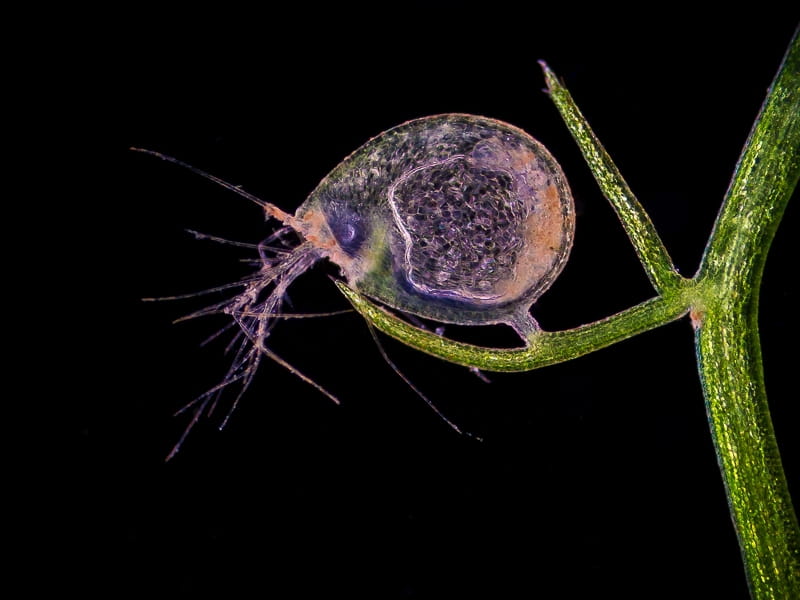
The bladder traps of bladderwort work through a complex system of hinged trapdoors that open when aquatic prey is sensed, allowing the prey to enter the trap. Once the prey is inside, several inwardly projecting hairs triggered a vacuum, drawing the prey into to the trap and holding it until it digests it. This trap is adapted to its diet of small aquatic organisms, which it gains nutrition from while its roots absorb sulfur, nitrogen, and other essential nutrients from the water.
Importance
The importance of bladderwort lies in its ability to draw nutrients from its environment. This plant is an important part of the aquatic ecosystem, serving as a biological filter, trapping suspended particles and releasing oxygen into the water. Additionally, bladderwort can be used as a biological control agent, limiting the population of some aquatic pests, such as mosquito larvae.
